With a project called FloodSENS, the Luxembourg-based company RSS-Hydro is now part of ESA’s InCubed programme. The project aims to develop an algorithm that efficiently identifies flooded areas under partial cloud coverage in optical satellite images, using Machine Learning and auxiliary high-resolution data from drones, digital elevation models, as well as water flow algorithms.
Floods are one of the most devastating natural disasters, accounting for the highest insured and uninsured losses annually, as well as costing many lives. The climate emergency intensifies the hydrological cycle. Consequently, the frequency and magnitude of extreme hydro-meteorological events, and therefore the risk of floods, are increasing, as confirmed to be happening in many places around the world. This flooding increase has devastating consequences, among which are a greater strain on humanitarian response efforts and the financial risk of the global (re)insurance market.
With the support of ESA InCubed programme, RSS-Hydro has now started to work on FloodSENS, a service that specifically addresses these issues by developing a flood mapping application for the open market that overcomes one of the major limitations of optical EO imagery during floods and is capable of efficiently scaling between optical satellite and drone images. Therefore this novel application would be able to efficiently reconstruct flooded areas under partial cloud cover in optical satellite images.
Guy Schumann, RSS-Hydro CEO, said: “This type of application is especially important for disaster response agencies at regional, national, and international level, who are keen to utilize the proliferation of open satellite data for flood mapping during emergencies. Additionally, in the insurance and re-insurance markets, stakeholders are interested in EO data to map the flood hazard of a high-impact event and, on a historical basis, to understand risk exposure and the changing nature of it.”
Bertrand Le Saux, ESA InCubed Technical Officer, added: “FloodSENS integrates both drone data and EO imagery with Machine Learning, to offer the best support to emergency response activities, as well as to the re-insurance market. At ESA, we see a big potential in this activity and we are ready to support it until its entry into the market”.
For Europe, but also for many other countries worldwide, future innovative EO-based and Machine Learning-powered apps would add considerable benefits to the existing products and services of the free Copernicus Emergency Management Service (EMS) and beyond. RSS-Hydro’s FloodSENS will position itself at the intersection of these two fields (EO technologies and Machine Learning application tools) and at the forefront of future EO-enabled innovative solutions, enabling a much more effective disaster response.
More information on the FloodSENS InCubed activity can be found here.
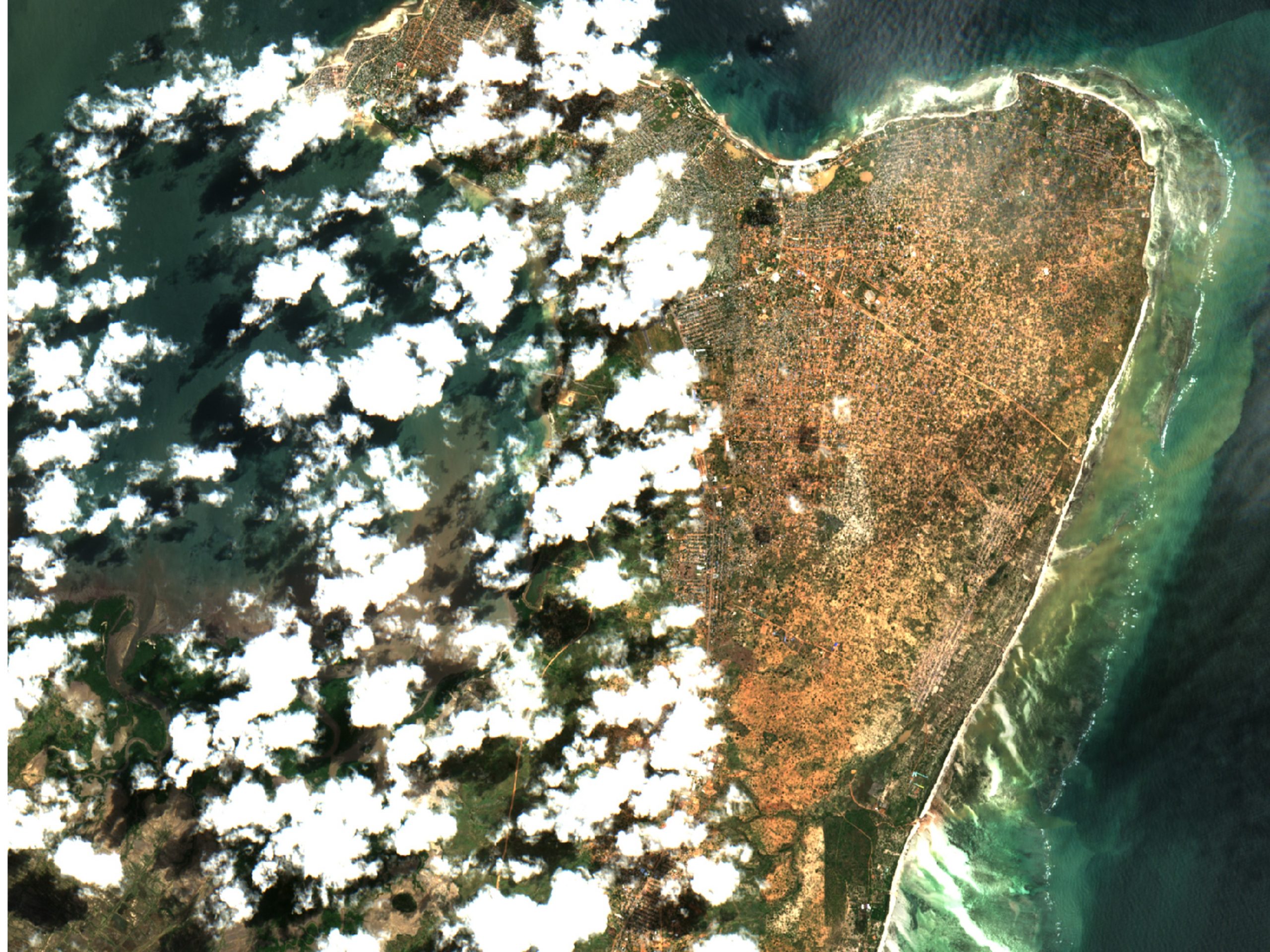
Image caption: The first half of 2019 was a devastating period for many countries in southeast Africa. After Cyclone Idai destroyed many places, in particular the port city of Beira, at the start of the year, Cyclone Kenneth ravaged northern Mozambique. Entire villages were destroyed and almost one million people were put at risk in the area. This partial cloud-free subset of a Sentinel-2 image from 3 May 2019 shows large areas under water in Pemba, regional capital of Cabo Delgado state, which experienced over 2 m of rain and flooding. FloodSENS will render optical imagery like this more usable during floods by reconstructing flooded areas under cloudy skies.
Links: FloodSENS, RSS-Hydro, Company Linkedin